P-Values
Another way of analyzing a hypothesis test is to consider P-values.
\[P=\text{Area to left of }\overline{x}\text{ in the sampling distribution}\]
We can find this P-value by using our Hypothesis Test Calculator or by first find the test value:
\[z=\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\sigma/\sqrt{n}}\]
The using our z-table to find the area to the left (similar for a t-distribution). The question remains when do we reject?
Well this depends on the test.
Two-Tailed Test
\[H_1:\,\mu\neq k\]
Do not reject \(H_0\) when
\[\frac{\alpha}{2}<\overline{x}<1-\frac{\alpha}{2}\]
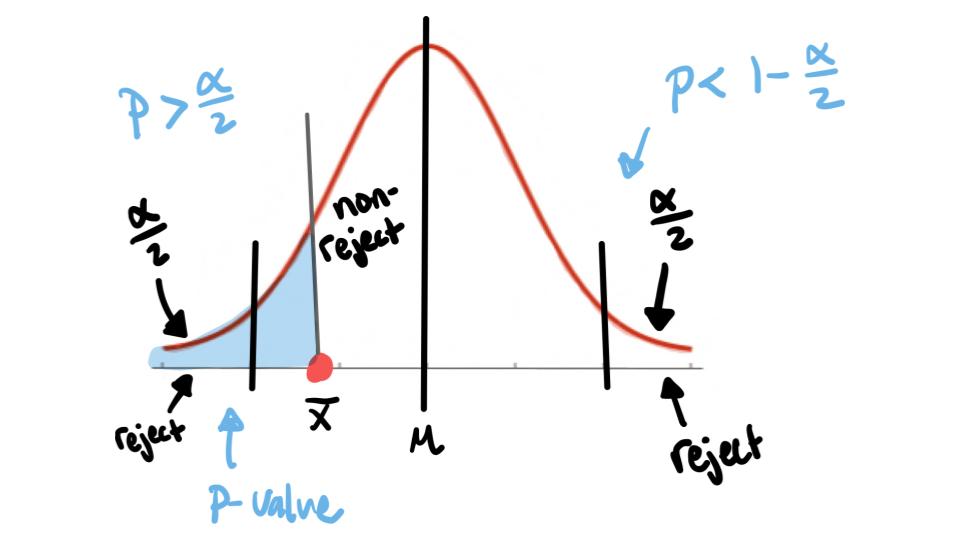
Reject \(H_0\) when
\[p<\frac{\alpha}{2}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{ or }1-\frac{\alpha}{2}<p\]
Left-Tailed Test
\[H_1:\mu<k\]
Do not reject \(H_0\) when
\[\alpha<p\]
.jpg)
Reject \(H_0\) when
\[\alpha>p\]
Right-Tailed Test
\[H_1:\mu>k\]
Do not reject \(H_0\) when
\[1-\alpha>p\]
.jpg)
Reject \(H_0\) when
\[1-\alpha<p\]